The healthcare industry is often risk-averse compared to other sectors when adopting new technologies, primarily due to the tough regulations the industry faces. However, mainly due to the Covid-19 pandemic, the industry has witnessed an acceleration in digital transformation, leading to improved efficiencies and enhanced patient outcomes.
Cloud computing is an already well-established technology in the industry, key to providing a faster, cheaper, and more agile approach to operating IT architecture and modernising enterprise applications. Healthcare companies can use the cloud across business functions, smoothing and accelerating operations and providing new possibilities in healthcare, such as decentralised clinical trials (DCTs).
Here we look at how cloud computing can both help and, in some cases hinder, companies in addressing some of the healthcare sector's challenges.
Drug discovery and development
In drug discovery and development, cloud computing allows for secure R&D collaborations between research teams. It simplifies data transfer from laboratory equipment and can enable scientists to analyse results and generate outcomes faster. There are many software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions to accelerate and improve drug discovery and development processes.
Pharma companies either use a vendor’s drug discovery and development SaaS solutions or develop software in partnership with a cloud vendor. Examples of cloud computing in drug discovery and development range from bioinformatic and Covid-19 vaccine platforms to cloud-operated remote R&D laboratories.
Cloud computing is also important in supporting other emerging technologies in drug discovery and development, such as big data and AI. Pharma companies often take advantage of the technology capabilities of their cloud vendors. For example, UCB collaborated with Microsoft in 2021 to use its cloud and AI solutions to improve the development of drugs in immunology and neurology. Also in 2021, Pfizer partnered with AWS to take advantage of its machine learning and cloud computing capabilities to accelerate drug discovery and development efforts.
Challenge | What’s happening? |
Productivity | Miners must ensure that they are increasing productivity by adopting the latest technology. Mechanization and monitoring are supporting improvements in productivity and lowering cost per unit output. |
Cost control | There is increasing upward pressure on costs to mining firms. Several factors have spurred this, including declining commodity prices, longer hail distances, falling ore grades, and rising material and labor costs. |
Supply chain | More disparate ore deposits are pushing mining into remote locations and developing nations. This gives rise to greater challenges in operating an efficient supply chain. |
Safety and sustainability | Given the worldwide shift to sustainability in the last few years, mining has come under increasing scrutiny for its damaging environmental practices. In addition, safety has become a concern. Mining firms must take more responsibility for ensuring that workers are properly protected on-site by taking active steps to avoid accidents and actively monitoring safety. |
Resource development | There is pressure on mining firms to continuously identify viable new mines. This is made more difficult by an environment of declining ore grades. Furthermore, there are rising development costs and more remote deposits. |
COVID-19 | COVID-19 has posed a massive threat to the mining industry. The main fear is that there could be an outbreak at a mine, which would force operations to a halt, impacting both costs and productivity greatly. This has led to operational challenges, including continuous testing of staff and reducing capacity at mines to enforce social distancing. |
Source: GlobalData Thematic Intelligence
Clinical trial design and recruitment
The traditional clinical trial model is inconvenient and taxing for patients, requiring them to visit hospital sites regularly, often with little compensation. Decentralised clinical trials (DCTs) offer an innovative solution to avoid scheduling conflicts, reduce or remove journey times, and improve the patient experience. Using digital technologies to bring research closer to patients’ homes (or other local settings), DCTs increase trial access, reducing the burden on participants by decreasing the number of physical site visits.
The number of DCTs has increased over the past ten years, from about 250 in 2012 to over 1,200 in 2022. Cloud computing is a key technology enabling the shift towards DCTs and, in turn, supports other technologies, including telemedicine, wearables, EHRs, and mobile applications.
Clinical trial operators can securely capture enormous clinical datasets in the cloud and effectively collaborate with stakeholders, such as investigators, contract research organisations (CROs), and sponsors. Cloud can also be used with AI and advanced data analytics to unlock clinical trial insights, leading to improved trial design and enhanced participant recruitment.
For example, SaaS provider Veeva System’s Veeva Vault Clinical Suite helps CROs and clinical trial sponsors with training, time management, randomisation in study designs, recruitment tracking, payments, and data capture.
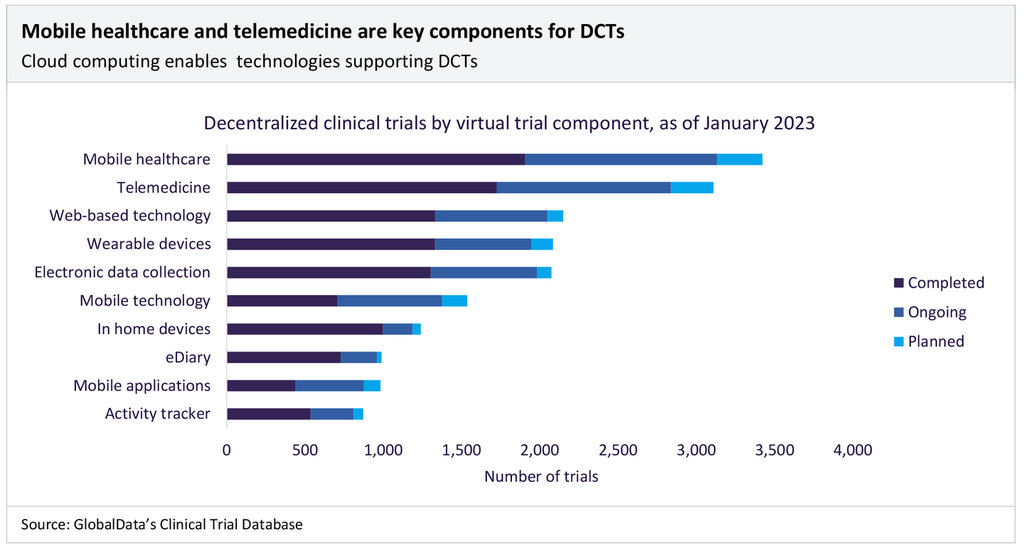
Source: GlobalData Thematic Intelligence
Supply chain disruption
GlobalData predicts that by 2035, supply chains will consist of cloud-based logistics services. Digitalising data collection in supply chains and moving it to the cloud provides companies with real-time insights into the state of a supply chain, helping them anticipate shortages, reduce errors, forecast demand, and enhance compliance checks and traceability.
Pharma companies can benefit the most from adopting cloud computing in supply chain management, particularly those producing complex drugs, such as vaccines and cell therapies, which require specific manufacturing processes, storage, and transportation conditions.
Regulation
Cloud computing can help companies across healthcare to comply with industry regulations.
Cloud computing can accelerate regulatory submission procedures for pharma and medical devices. Companies can provide regulatory bodies with secure links to the necessary data and information on servers instead of the lengthy process of assembling dossiers.
This also supports expanded approvals and pharmacovigilance for pharma, as new data can be submitted directly to the cloud for real-time analysis by regulatory bodies (for example, through the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) MyStudies app).
Cloud-based apps can also help pharma to track drug side effects and encourage patients to receive treatment. For example, Oracle worked with the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to create the v-safe health check app. Any person that received a Covid-19 vaccination registered on the app and voluntarily reported side effects. This helped the CDC to gather real-world evidence on how populations responded to the vaccine. Medical journals then used the study results to counteract misinformation online and reassure pregnant patients that the Covid-19 vaccine was safe.
However, cloud computing could also pose a risk to a healthcare organisation’s ability to comply with regulations. As discovered in a publication by Morais et al. (2022), security and privacy are the two biggest challenges related to cloud computing adoption by healthcare. Moving data from in-house corporate data centres to the cloud can expose companies to a higher risk of data misuse, as data is no longer stored and secured behind company firewalls.
However, given the scale of global cloud vendors, such as Oracle, Microsoft Azure, and AWS, these vendors can afford the best cybersecurity practices and hire much larger cybersecurity and data governance teams than most healthcare organisations. Therefore, for healthcare organisations, cloud vendors can provide a much easier, more secure, and cheaper way of complying with data privacy regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Cloud computing impact assessment: pharma
The following section looks at the areas in cloud computing where pharma companies could invest. The matrix below details the areas in cloud computing where pharma companies should focus their time and resources. We suggest that pharma companies invest in technologies shaded in green, explore the prospect of investing in technologies shaded in yellow, and ignore areas shaded in red.
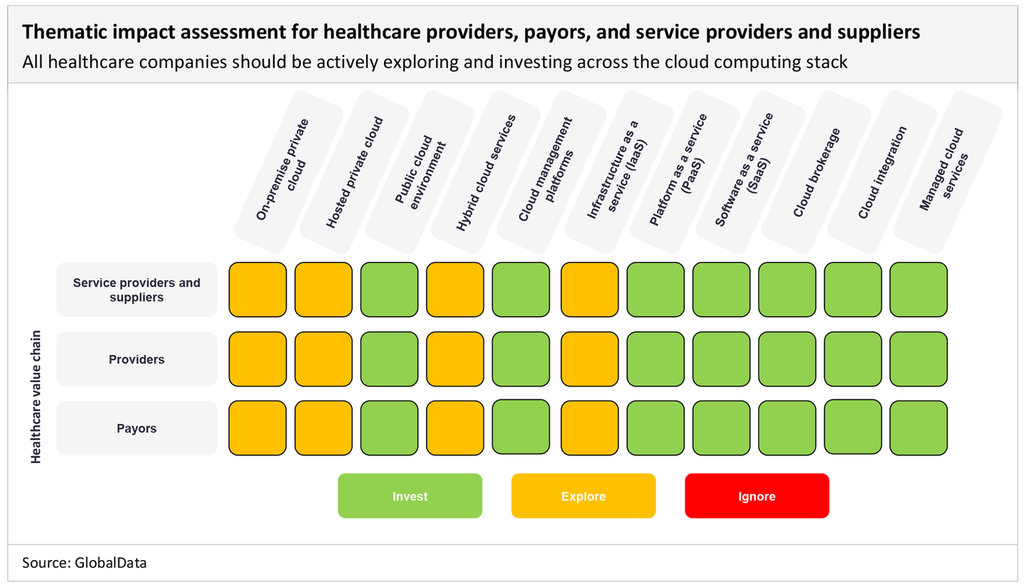
Pharma companies must invest significantly in cloud computing across their value chains. Cloud computing provides various benefits, from securing R&A collaborations between research teams and capturing big data sets from clinical trials to accelerating regulatory submission procedures and improving sales data collection.
As well as investing in specialised SaaS solutions, pharma companies can invest in PaaS to develop software tailored to their specific R&D or business goals. Larger pharma companies can also consider investment in IaaS to develop proprietary platforms in collaboration with a cloud vendor, upon which their own software can be created.
Pharma companies face the same pressures as healthcare providers and payors regarding patient data privacy and sovereignty. On-premises private clouds will suit large pharma with vast operations, but hosted private clouds will be more cost-effective and provide easier management. Public clouds offer the most cost-effective solution, while multi-cloud environments are increasingly popular in the industry.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Thematic Intelligence uses proprietary data, research, and analysis to provide a forward-looking perspective on the key themes that will shape the future of the world’s largest industries and the organisations within them.