Image: Atomwise CEO and co-founder Abraham Heifets
Drinking alcohol raises risk of oesophageal and other cancers
Recent studies have further solidified drinking alcohol as a major risk factor for oesophageal and other forms of cancer.
Dr Judith M. Sills. Credit: Arriello
Dr Eric Caugant. Credit: Arriello
Oesophageal cancer is the sixth most common cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Despite advances in the treatment of oesophageal cancer, only 10%-15% of patients survive at least five years after diagnosis.
An umbrella review published in Nature Communications in late July found strong or highly suggestive evidence that alcohol consumption raises the risk of several types of cancer, including oesophageal cancer. These results further solidify drinking alcohol as a major risk factor for cancer and could inform more targeted public health policies that encourage people to limit their intake.
Papadimitriou and colleagues reviewed 860 meta-analyses that examined associations between a number of dietary factors and the risk of 11 types of cancer. The authors also graded the evidence for each association as strong, highly suggestive, suggestive or weak.
Drinking alcohol raised the risk of oesophageal cancer among men by 33% (22%-46%), an association that was highly suggestive using their grading criteria. The evidence was also strong or highly suggestive for alcohol consumption and colorectal, breast, head and neck and liver cancer.
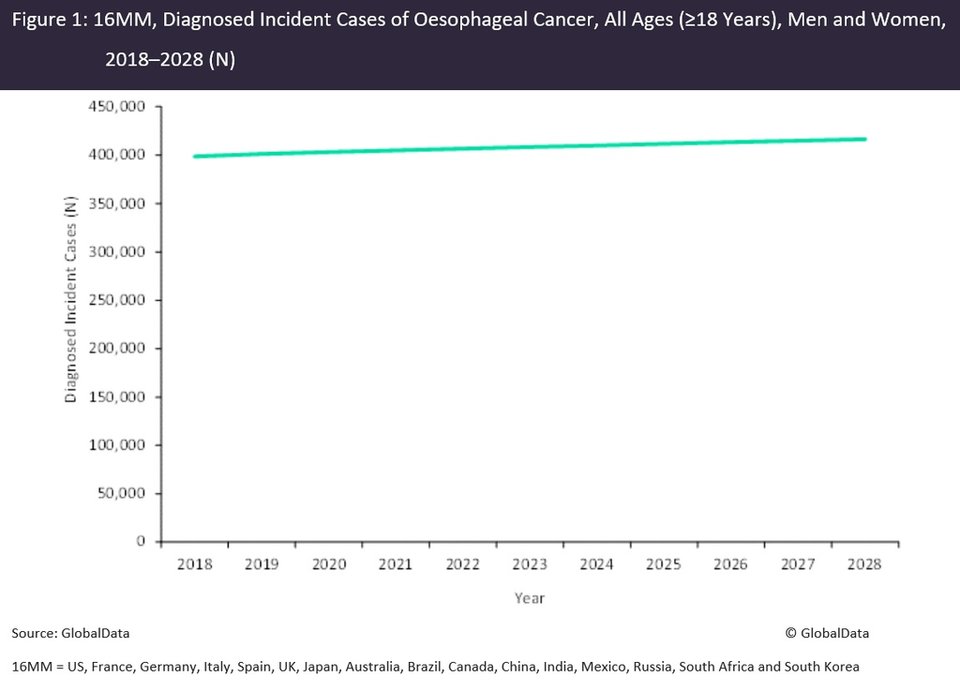
In the 16 major pharmaceutical markets (16MM: US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK, Japan, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, India, Mexico, Russia, South Africa and South Korea), GlobalData epidemiologists expect an increase in the diagnosed incident cases of oesophageal cancer over the next decade, with cases approaching 420,000 in 2028.
The results of this most recent study could inform public health policies that better target alcohol consumption and other modifiable risk factors for cancer. If such practices are widely adopted, new cases of esophageal cancer would be prevented, leading to incident cases below those currently forecast.
Diet is a major, potentially modifiable risk factor that can help prevent the development of oesophageal and other types of cancer. While alcohol raised cancer risk, the study also found that drinking coffee and eating fruits and vegetables reduced the risk of several cancers.
GlobalData epidemiologists recommend continued monitoring of trends in the incidence of oesophageal cancer and additional studies to better understand the mechanism behind its link with alcohol. These findings do, however, point to drinking less alcohol as one way to help prevent cancer.
For pharmaceutical industry data, comment and analysis, visit GlobalData's Pharmaceuticals Intelligence Centre.
market insight from