COMPANY INSIGHT
Sponsored by Mimotopes
Custom Peptide Synthesis, Peptide Libraries and Reagents

Mimotopes provides custom peptide synthesis, catalogue peptides, PepSet™ peptide libraries, reagents, antibodies, and an array of other immunology services for the research market.
We offer a range of options for customisation and modification to ensure our products meet the highest customer standards.
Custom peptide synthesis
Mimotopes supplies custom peptides with fully customisable sequences and modifications, including options for the N and C termini.
Our initial feasibility assessment includes information on the predicted peptide solubility and potential difficulties in custom peptide synthesis, which allows for customer involvement at every stage of the design process. With our careful consultation, the end product should meet the specifications of the project.
Custom peptides are an invaluable tool in numerous fields of research, including immunology and drug development projects. Additionally, labels and modifications can make a standard peptide versatile and adaptable to any purpose.
PepSet peptide libraries
As one of the prominent applications of combinatorial chemistry, parallel synthesis techniques allow hundreds of peptides to be synthesised simultaneously into PepSet peptide libraries. Mimotopes’ time-saving strategies economically produce entire peptide libraries with the same customisation options as a single custom peptide.
Suitable for applications such as epitope mapping and screening, a variety of PepSet preset combinatorial library and array styles are available. These include overlapping peptides, alanine scanning, combinatorial positional scanning, truncated peptide libraries, and scrambled peptide libraries, as well as combinatorial libraries comprised of more than one different type.
Peptide libraries are an underutilised resource. From affirming new leads with a scrambled library to identifying essential residues, a PepSet peptide library can offer more than the sum of its peptides.
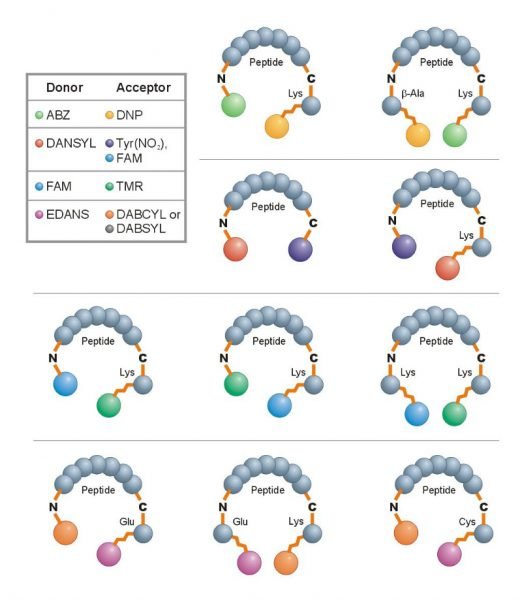
Peptide labels and modifications
With labels and modifications, changes can be made to a peptide without altering the base amino acid sequence. This versatility allows similar peptides to function in different ways and, in some cases, lead to complete inhibition.
Cyclisation
Cyclisation is an optional modification, to aid in the constrained conformation of a peptide with a disulphide bond. We offer head-to-tail cyclisation, side-chain cyclisation, stapled, and other constrained peptides. Linear peptides, especially those with long sequences, are particularly unpredictable and susceptible to unintentional folding. Cyclised peptides, on the other hand, are more stable.
Bio-conjugation of peptides
Conjugation of a peptide to another molecule, such as an immunogenic carrier protein or oligo has broad applications in immunological and molecular research. Bifunctional pegylation also has applications in pharmacology.
Peptides generally don’t produce an antigenic response on their own, so conjugation facilitates a way to produce anti-peptide antibodies by coupling to a T-cell carrier protein.
Biotinylation
In immunological research and screening applications, capture mechanisms may require biotinylated peptide synthesis. Biotinylation is the addition of a biotin group to the terminus or side chain of a peptide to allow for binding to avidin and streptavidin. This complex is advantageous for the immobilisation of a peptide library, particularly for use in multiple assays.
Phosphorylation
In biological research applications, phosphorylation is a fundamental process. Mimotopes offers phosphopeptide synthesis for cell research, as well as phosphopeptides to be used as antigens in the production of anti-phosphopeptide antibodies.
Methylation, carbamylation, acetylation and glycosylation
Mimotopes offers several optional peptide modifications including carbamylation, glycosylation, methylation and acetylation. These are useful in a wide variety of applications. Peptide methylation, the addition of at least one methyl group, can have applications in epigenetics.
Fluorescent labels and REPLI library
A fluorescent peptide is used in biological experiments to detect a reaction or change. We provide FRET peptides in our REPLI PepSet peptide libraries, fluorescently labelled with an inhibitor for cleavage reactions so that there will be visible fluorescence when cleavage has occurred.
Stable isotope-labelled peptides
Isotope-labelled peptides are often indistinguishable from unlabelled peptides, except under specific conditions. This flexibility allows use in a range of applications, including as a reference in mass spectrometry.
Peptide reagents
Mimotopes supplies and distributes peptide reagents and chemicals both within and outside of Australia. Mimotopes’ range of amino acids includes unusual amino acids, β amino acids, F-moc protected and Boc-protected amino acids.
Our complete catalogue also includes tools, coupling reagents, resins, activators such as HATU and HBTU, as well as other supplies for solid phase and liquid phase peptide synthesis.
Immunology services
In addition to custom and catalogue peptides, Mimotopes also supplies monoclonal and custom polyclonal antibodies. Other immunological services, such as T-cell epitope mapping and B-cell epitope mapping, can be achieved with the use of our PepSet peptide libraries.
Contact information
Mimotopes
Suite 1, Unit 9 / 677 Springvale Rd,
Mulgrave, VIC 3170 Australia
Tel: +61 3 9565 1111
Email: mimotopes@mimotopes.com
Website: www.mimotopes.com